Disassociating From the Beginning: US Senators Propose a Ban on Cultivated Meat in School Meals
7 Mins Read
Amid a flurry of proposed bans on cultivated meat in the US and around the world, two senators have now introduced a bill that would prohibit the use of cultured meat in school meals.
Just as American schoolchildren are having to fight for even soy milk under the First Amendment, two US lawmakers are hoping to introduce a wider crackdown on alternative proteins in the education sector.
Senators Mike Rounds (Republican) and Jon Tester (Democrat) have proposed a bill to amend the Richard B Russell National School Lunch Act and the Child Nutrition Act of 1966 and ban the use of cultivated meat in US school meals.
Titled the School Lunch Integrity Act of 2024, the senators seek to prohibit cell-cultured meat from being served in schools under the National School Lunch Program (NSLP) and the School Breakfast Program (SBP).
“This common-sense bill will make sure our schools can serve real meat from our ranchers, not a fake substitute that’s grown in a lab,” said Tester, a third-generation farmer from Montana. “Montana ranchers grow the best meat in the world, that’s a fact – and our students ought to be getting the best in their school breakfasts and lunches every day.”
US senator promotes local beef over cultivated meat

Cultivated meat has already been approved for sale in the country, with the USDA granting clearance to Californian producers UPSIDE Foods and GOOD Meat last year. It made the US only the second nation to allow the consumption of these proteins – but Rounds’ office claimed that these actions “undermine the important work of American livestock producers”.
The USDA hasn’t yet issued any guidance over cultivated protein in the NSLP or SBP, but despite its approval of cell-based chicken from the aforementioned companies – which have also received a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) certification from the FDA – Rounds questioned the safety of these products, citing a lack of research.
“It starts out with a piece of meat, a cell from an actual chicken and then it is developed artificially within the laboratory. We just want to make sure that’s not the stuff they are selling in our schools,” Rounds told local outlet Keloland.
In a statement, he said: “Our students should not be test subjects for cell-cultivated ‘meat’ experiments. South Dakota farmers and ranchers work hard to produce high-quality beef products. These products are often sold to South Dakota schools, where they provide necessary nutrition to our students.
“With high-quality, local beef readily available for our students, there’s no reason to be serving fake, lab-grown meat products in the cafeteria. I’m pleased to introduce this bipartisan legislation that benefits South Dakota producers and protects students from the unknown effects of cell-cultivated ‘meat’ products.”
Reflecting a wider disconnect between meat and climate change
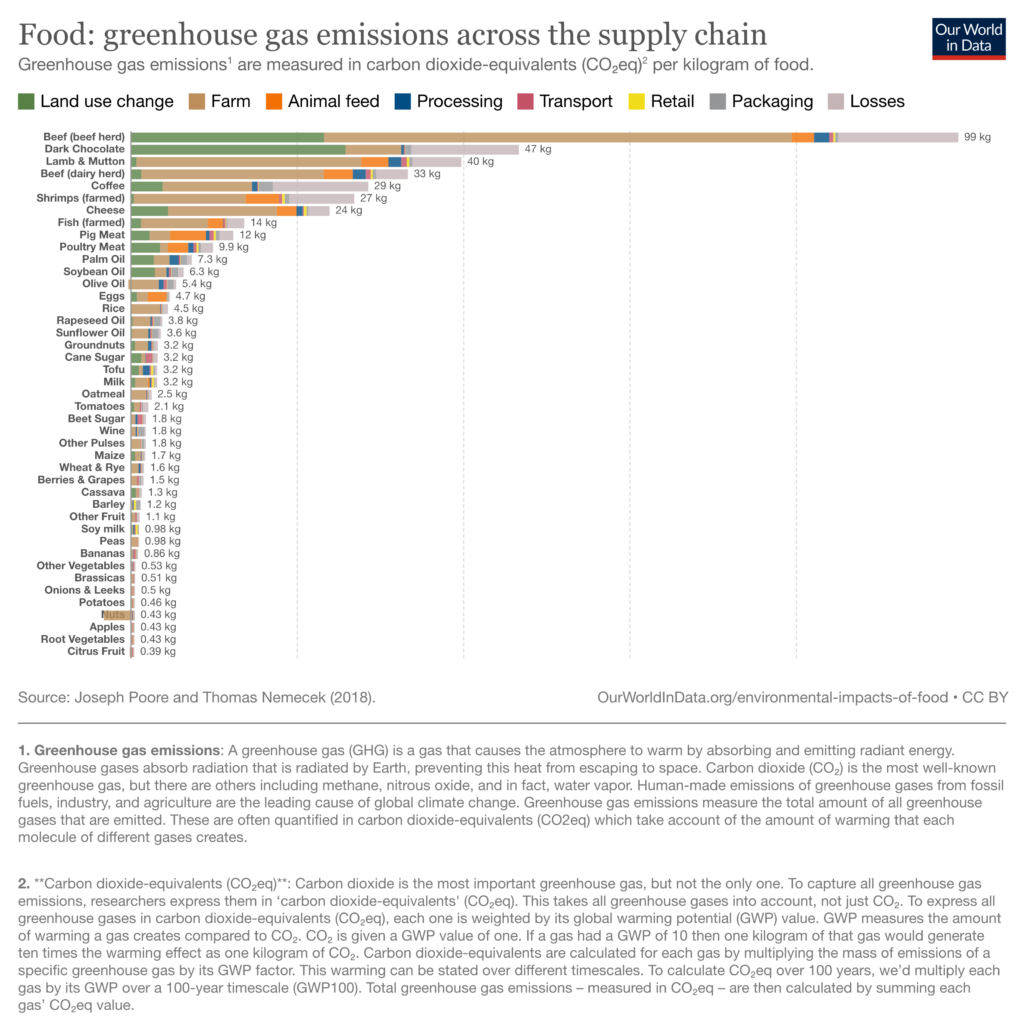
It’s a rhetoric commonly used by sceptics of cultivated meat, which – as mentioned above – has been cleared as safe for human consumption by the US government. Promoting beef serves the interests of the country’s livestock industry – which receives 800 times more public funding than alternative protein companies – and encourages the consumption of a product that is proven to be the worst-emitting food.
Rounds will argue that he’s supporting local farmers and beef, which will have a lower carbon footprint than meat produced elsewhere. This is a commonly held misconception, because transport accounts for less than 1% of beef’s GHG emissions. “Eating local beef or lamb has many times the carbon footprint of most other foods. Whether they are grown locally or shipped from the other side of the world matters very little for total emissions,” explains Our World in Data’s Hannah Ritchie.
But perhaps Rounds can be forgiven for the confusion – he is, after all, a lawmaker in a country that fails to connect meat consumption with the climate crisis. One study found that 74% of Americans don’t think eating meat is bad for the environment, while another put that number at 41% for red meat. But peer-reviewed research has revealed that, when produced using renewable energy, cultivated meat can account for 92% fewer emissions, 94% less air pollution, and 90% less land use than conventional beef.
Even studies that critics routinely cite – such as a 2019 University of Oxford paper – are misinterpreted. While that research was undertaken when cultivated meat was much less developed and heavily reliant on fossil fuel power, it still found that the worst-case scenario for cultivated meat’s GHG emissions is better than the “best” conventional meat production systems for at least the next 100 years.
Livestock industry questions the safety of cultivated meat
Nevertheless, the bill was welcomed by animal agriculture groups like the US Cattlemen’s Association, R-CALF USA, National Cattlemen’s Beef Association and South Dakota Pork Producers, who seemingly ignored the implications of the safety rulings for cultivated chicken – a marker that other foods produced this way can also be regulated the same way in the future – by the USDA and FDA. In January, Israel became the first country to approve the sale of cultivated beef, after the Israeli Ministry of Health (IMOH) issued a ‘no questions’ letter for Aleph Farms.
“Science experiments belong in the classroom, not the cafeteria,” said Justin Tupper, president of the US Cattlemen’s Association. “The long-term health effects of consuming foods produced using cell-cultured technology [have] not been established. These products are too new and untested to be considered safe for our nation’s children.”
Bill Bullard, CEO of R-CALF USA, added: “The claim that cell-cultivated meat grown in a laboratory is as safe and healthful as real, natural meat has not yet been definitively determined. So, subjecting children to this nascent, scientific experiment is bad public policy. We applaud Senator Rounds’ bill that will ensure our children and grandchildren will not be encouraged to consume this controversial and unnatural product while at school.”
“We just want to make sure that our livestock producers in the upper midwest aren’t ham-stringed by schools suggesting that because of liberals in the area or individuals that don’t like ag that they are suddenly then being challenged to compete with cultured meat, which we think has a long way to go and hasn’t been properly tested at this stage of the game,” added Rounds.
Joining a global trend of cultivated meat bans

The legislation is reminiscent of the amendment of France’s climate law in 2021, which banned cultivated meat in canteens, similarly calling into question the safety of the products and the threat to livestock farmers.
That wasn’t the end of France’s anti-cultivated-meat push, which last year introduced a bill to prohibit the production and sale of these novel proteins throughout the country – not just in the education sector.
It’s part of a wider trend that’s developing around the world. A month before France’s proposal, Italy became the world’s first country to officially ban cultivated meat. And one of the farming groups that lobbied prominently for the law is now in talks with Hungary to push forward similar legislation in the country.
Austria has also voiced its opinion against cultivated meat, presenting a note to the EU’s Agriculture and Fisheries Council last week alongside Italy and France. It garnered support from the Czech Republic, Cyprus, Greece, Hungary, Luxembourg, Malta, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Spain.
Meanwhile, senators in the US have been jumping on this bandwagon as well. Before Rounds and Tester introduced their legislation to the Senate, Republican lawmakers in several states had already floated the idea of prohibiting the general production and sale of cultivated meat within state borders.
It began with Florida, where House representative Tyler Sirois proposed HB 435, which seeks to ban the production, sale, holding and distribution of cultured meat within the state, imposing criminal penalties – including facing misdemeanours of the second degree, fines of $500 to $1,000, and license suspensions or stop-sale orders – on anyone violating these rules.
Shortly after, Texas governor Greg Abbott signed a bill requiring clear labelling of plant-based and cultivated meat, seafood and egg products, while Nebraska’s Real MEAT Act would mandate the word “imitation” on alt-protein if passed.
Then, in Arizona, House representative Quang Nguyen drafted HB 2244, a bill that would make it illegal to “intentionally misbrand or misrepresent” an alternative meat product as meat, while fellow Republican David Marshall went a step further with HB 2121, attempting to ban the sale or production of cultured meat.
And just this week, Wisconsin State Assembly representative Peter Schmidt – a Republican dairy farmer – proposed two bills against alternative protein, one of which put restrictions on the labelling of cultivated meat.
Rounds said it’s too early to tell how the bill will play out in the Senate. But really, the focus should be on finding ways to safeguard the environment, not promote food production methods that destroy it. Climate activists will hope these bills stop making the rounds.




